
Background and Summary
One of the key goals of achieving Universal Health Coverage is financial protection i.e., affordable health services at low costs for every individual particularly funded through public sources, as recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO). This leads to equity in financial contribution and distribution of risk amongst both healthy and sick in society.

As per National Health Account 2015-16, it is estimated that out of pocket expenditures (OOPE) comprise over 60% of the total health expenditures in India leading to catastrophic payments and crippling poverty for families seeking hospitalisation. Due to this every year, over 60 million Indians fall below the poverty line. Lack of access to good quality tertiary care services has directly affected the sick, elderly and women in families preventing them from seeking timely care. It has forced people to either avoid treatment for years or further aggravated chronic conditions.
Ayushman Bharat, under its second component, Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) was launched in September 2018 as an aim to address some of these challenges and subsuming the earlier scheme of Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana (RSBY).


AB PM-JAY, the flagship program of Government of India, provides an annual health assurance cover of Rs. 5 lakhs per family for secondary and tertiary care hospitalizations addressing 10.74 Cr total families that form the lowest 40% population in the country. The eligibility criteria are based on the Socio-Economic Caste Census database 2011. Having entered into its fourth year of implementation across 33 States & UTs, the scheme has since created 13 Crores Ayushman cards, provided treatment to 2.9 Cr beneficiaries, and empanelled over 28k public and private hospitals. Treatment has been provided under 1570 packages comprising both medical and surgical.
Current Scenario
The above numbers also reflect the progress the scheme has made to create a demand led healthcare pattern and to strengthen health systems within the country along the building blocks defined by the WHO. I highlight a few points as below:
1. Financing – While RSBY scheme had a health cover of Rs. 30,000 per family (with maximum capping of 5) based on enrolment criteria, Ayushman Bharat is an entitlement-based scheme providing a cover of Rs 5 lakhs annually per family with no upper capping on family size. This has shown to reduce gender gap and benefitting women where earlier it was observed that large families preferred male members first as beneficiaries. In 2014 where 6.6 Cr families were covered, there are almost 14Cr families covered today including the State schemes under PM-JAY.
2. Service Delivery – There are approximately 26,000 hospitals empanelled under PM-JAY (51% public hospitals and 48% private hospitals) ranging across single speciality and multi-specialty health care providers (HCPs). The advent of this scheme has also seen a rise in the number of hospitals built in tier-2 and tier-3 cities, creating health infrastructure in underserved areas. The Ayushman Bharat fund pool generated in public hospitals is being utilised for improvement in infrastructure, equipment and capacity or strengthening manpower. Many states like Chhattisgarh, Gujarat have implemented the same. To encourage quality standards of healthcare providers, 9% of hospitals have attained NABH standard through incentivised structure. Additionally, patient centric care is nurtured by patient-provider feedback with a 24-hour helpline number (14555) comprising of 100+ call centre team.
3. Health workforce – As a consequence of scheme utilization, considerable employment opportunities have been created across the government sector, private hospitals, insurance companies, third-party vendors etc. AB PM-JAY has also improved institutional capacity by 50% in most State Health Agencies with a skilled team of doctors, auditors, administrators as well as set-up 100+ District Implementation Units (DIUSs). To curb fraud, abuse and malpractices, an anti-fraud unit has been set up both nationally National Anti-Fraud Unit (NAFU) and at state (SAFU) which was a missing component of the earlier schemes resulting in action against 400 hospitals and savings over R. 12 Cr to the beneficiaries.
4. Health Information System – A robust IT platform forms the backbone of the AB PM-JAY scheme that runs across beneficiary identification (BIS), hospital empanelment (HEM), claims processing (TMS), frauds detection (RADAR, FACTS) as well as scheme monitoring dashboards (INSIGHTS). This has led to a cashless and paperless scheme along with building a strong database in tracking utilization trends, facilitating provider payment mechanisms, disease management etc.
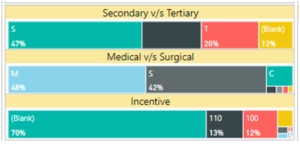
5. Access to essential medicines and treatments – 59% of the treatment amount comprises of tertiary care hospitalizations with the top three services being oncology, cardiovascular and orthopaedic speciality. The 1500+ packages under Ayushman Bharat are very comprehensive and cover 24 specialties. With the introduction of portability, over 2 lakh beneficiaries are able to seek treatment outside their home state in national hospitals like AIIMS, Safdarjung, PGIMER etc.
By extending health coverage to remaining populations beyond PM-JAY, many States like Karnataka, Uttarakahand, Chhattisgarh have expanded beneficiary base and attained universal health coverage. These States have also reached 90% of families with at least one Ayushman card reflecting greater awareness. As part of beneficiary expansion, NHA has entered partnership with various schemes like Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi-Health Ministers Discretionary Grant (RAN-HMDG), Building and Construction Workers (BoCW).
Way Forward
Ayushman Bharat recognizes the importance of reaching UHC central to achieving Sustainable Development Goals ensuring good health and well-being for all. Besides financial protection, the other two pillars of UHC are equity i.e. access to health services relative to need and quality i.e. strengthened services such as medical staff, medicines, hospitals etc.
Health systems strengthening forms an integral part of attaining UHC. AB PM-JAY is now looking at these various initiatives to improve the same:
• Expanding beneficiary base– Moving to the National Food Security Act (NFSA) database that would help PM-JAY cover 70% of the poor and vulnerable population who are Ration card holders.
• Convergence with national schemes–To avoid overlap of families in more than one scheme, uniformity of data, robust IT platform and improved access to services, NHA is moving towards converging with various health schemes catering to different populations or diseases such Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY), ESIC, BoCW, CGHS and RAN-HMDG.
• Disease management – As the scheme moves into the next phase, it is important to continue to do evaluation studies to see the impact of the scheme on health seeking behaviour. With increasing Non-Communicable Diseases burden, studying utilization trends will help in promotive and preventive care.
• Continuum of Care and Health ID– A path-breaking initiative to improve health systems is to connect Health and Wellness Centres to secondary and tertiary care centres through a referral mechanism. This can be done through the Health IDs that are being developed under the National Digital Health Mission.
Conclusion
Like the herculean task of building a ship while it’s sailing, Ayushman Bharat has made great strides in improving health systems in India and yet has just scratched the surface with many more milestones to go. The current pandemic has exposed several loopholes in our health system but with continued political will, good governance, and better healthcare expenditures it will not be far-fetched to envision a day when every citizen in India has access to state of the art healthcare providers regardless of need and financial status.
Views expressed by Shubhashree Patra, Young Professional, National Health Authority (NHA)
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter , Instagram.












