Dr Sandeep Attawar, Director, Cardiac Surgery and Thoracic Organ Transplantation, Fortis Memorial Research Institute
Dr Nikhil Kumar, Director, Cardiology, Fortis Memorial Research Institute
Dr Sharad Tandon, Director “ Non Invasive Cardiology, Fortis Healthcare
Of late, of advances have taken place in the field of invasive cardiology in order to keep pace with management of complex cardiac disorders. The major advances are catheter based exclusion of LAA to prevent stroke and the role of Renal denervation therapy in uncontrolled hypertension, wearable cardioverter defibrillator, optical coherence tomography, Strain Imaging and hand held echo machine.

Catheter based exclusion of LAA
Patient with lone or non-valvular AF are prone to have embolic strokes despite anticoagulant therapy. Ongoing search of many years has led to development of catheter based treatment in order to prevent stroke. WATCHMAN LAA occluder has shown reduction in stroke incidence and also in cardiovascular mortality as compared to warfarin in PROTECT AF trial and awaiting FDA approval. Device is deployed through transseptal technique. Other emerging devices like occlutech, coherex, etc, are under trial.
With increased incidence of uncontrolled primary hypertension, as a result of noncompliance, there was a desperate need of alternative therapy. Renal denervation therapy has shown benefit in controlling blood pressure and also increasing compliance among patients because of decrease in number of antihypertensive medicines. It requires radiofrequency ablation of bilateral renal sympathetic afferent and efferent nerves which travel across the renal arteries.
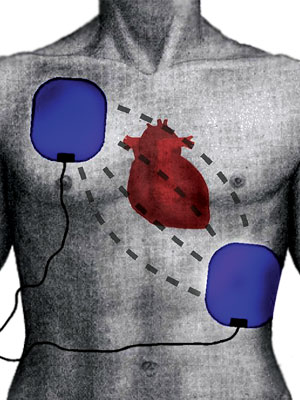
Wearable Cardioverter defibrillator
The wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) is an effective option for external monitoring and defibrillation in patients at risk for sudden cardiac arrest caused by ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation and who are not candidates for or who refuse an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD).

The device has been used when a patients condition delays or prohibits ICD implantation, or as a bridge during periods when an indicated ICD must be explanted, such as for treatment of infection.
The WCD has been increasingly used for primary prevention of sudden cardiac death during the high risk gap periods early after myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization with coronary artery bypass graft or percutaneous coronary intervention, or new diagnosis of heart failure, when its use is as a protective bridge to ICD or left ventricular improvement.
The WCD can also provide monitoring with backup defibrillation protection during diagnosis and risk stratification periods.
Although compliance and absence of pacing capability are limitations, shock efficacy and overall survival seem similar with a WCD compared with ICDs, and studies have reported satisfactory overall compliance.
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a diagnostic procedure that is used in combination with a procedure called cardiac catheterization. The technique uses near-infrared light to create images of the inside of your blood vessels. Unlike ultrasound, which uses sound waves to produce an image of the blood vessels, OCT uses light. With OCT, doctors can obtain images of the blood vessels that are about the same as if they were looking under a microscope.
How does it work?
OCT uses near-infrared light to create images of the inside of the coronary arteries. The technique delivers such high-resolution images because it uses light instead of sound waves. In fact, OCT allows cardiologists to see in 10 times more detail the inside an artery than if they were using intravascular ultrasound.
OCT is used along with heart catheterization procedures, including angioplasty, in which cardiologists use a tiny balloon on the tip of a catheter to unblock a coronary artery. Most patients who undergo balloon angioplasty also receive a stent-a small mesh-like device placed inside the artery to keep it open. OCT images can help cardiologists see if a stent is holding an artery open and whether the stent is positioned correctly against the artery wall. OCT also lets cardiologists clearly see the plaque inside an artery, find out how much fat or clot is inside an artery, and take precise measurements before and after placing stents.
The main applications of the OCT system are atherosclerotic plaque assessment, Stent struts coverage and apposition assessment, and in stent restenosis uation, PCI guide and optimisation, in case of bio absorbable stents, information regarding the time course of stent dissolution.
Hand Held/ Pocketsize ECHO machine
An echocardiography system that conveniently slips into a coat pocket might seem a natural for cardiologists: a readily available window into the heart and how its functioning, far more informative and flashy than the venerable stethoscope.
The pocket-sized echo system provides additive clinical value over the physical examination, contributing to an increased number of diagnoses, reducing the performance of unnecessary conventional echocardiographic studies and allows many patients to be released from the outpatient clinic / Emergency rooms without the need for further testing after the initial consultation.
Pocket-size hand-held echocardiographic (PHHE) devices are extremely mobile, providing the fundamentals for increased use of cardiac imaging in the diagnostics of patients. l They are suitable for a quick assessment of cardiac structures and function. l They are capable of high-quality recordings, with best accuracy for the assessment of left and right ventricular function, as well as the detection of pericardial or pleural effusions. l They are suitable for semi quantitative uation of valvular morphology and valvular function if equipped with color Doppler. l PHHE devices are also suitable for non-cardiac imaging in Emergency room settings. l A proper level of competence and skills are mandatory before using the technology.
Strain Imaging
Echocardiographic strain imaging, also known as deformation imaging, has been developed as a means to objectively quantify regional functions of heart. First introduced as post-processing of tissue velocity Doppler imaging converted to strain and strain rate, strain imaging has more recently also been derived from digital speckle tracking analysis. Strain imaging has been used to gain greater understanding into the pathophysiology of cardiac ischemia and infarction, primary diseases of the heart muscle, and the effects of valvular disease on heart function, and to advance our understanding of diastolic function
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter , Instagram.












