What is high blood pressure?
Blood pressure (BP) is the force of your blood against the walls of your blood vessels as your heart pumps blood around your body. If this pressure becomes high, you are said to have high blood pressure, or hypertension.

Blood pressure is expressed by two measurements, the systolic and diastolic pressures, which are the maximum and minimum pressures, respectively.For most adults, normal blood pressure at rest is within the range of 100–130 millimeters mercury (mmHg) systolic and 60–80 mmHg diastolic. Depending on how high the BP is above normal, it is classified as stage I, stage 2 and critical as shown in the table. 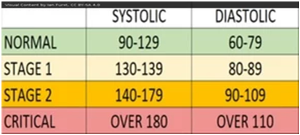
High BP is classified as primary (when no specific cause can be identified) or secondary (when there is an underlying cause). The most common cause of secondary hypertension is kidney disease. Therefore, every individual found to have high BP must be evaluated for kidney disease.
The problem of high BP is huge not only in our country but all over the world. According to a survey of more than 4000 people from urban as well rural pockets conducted by Narmada kidney foundation, about 40% were found to be hypertensive. More worryingly, BP was uncontrolled in more than 50% of hypertensive subjects.

How does one know that he/she has high BP?
High BP typically has no symptoms. Some may get repeated headaches. The only way to know if one has high blood pressure is to test for it. High BP is not diagnosed based on just one reading.
 Typically, three elevated readings are needed to confirm the diagnosis. Those diagnosed to have high BP must monitor frequently at home. If uncontrolled, it causes progressive harm to the cardiovascular system. When blood pushes with too much force through the cardiovascular system, it can damage the walls of the arteries as well as the heart muscle. Damage to the arteries that supply the heart muscle with blood can eventually contribute to a heart attack. Similarly, damage to the arteries that supply the brain with blood can contribute to a stroke, and damage to the arteries that provide the kidneys with blood can lead to kidney disease.
Typically, three elevated readings are needed to confirm the diagnosis. Those diagnosed to have high BP must monitor frequently at home. If uncontrolled, it causes progressive harm to the cardiovascular system. When blood pushes with too much force through the cardiovascular system, it can damage the walls of the arteries as well as the heart muscle. Damage to the arteries that supply the heart muscle with blood can eventually contribute to a heart attack. Similarly, damage to the arteries that supply the brain with blood can contribute to a stroke, and damage to the arteries that provide the kidneys with blood can lead to kidney disease.
How is high BP treated?
For treatment of high BP, one must first find out the cause. If the cause can be identified, treating the cause will get BP to normal. If the cause cannot be identified, lifestyle changes (exercise, weight loss, salt reduction, quitting smoking and stress reduction) can help lower blood pressure. If even after lifestyle changes BP remains high, one must take BP lowering medication regularly to keep BP in control. To know if BP is controlled, one must monitor BP at home regularly with the help of simple digital monitor.
Also read: Work stress and bad sleep pose risk to high BP patients: Study
What is chronic kidney disease?
Chronic kidney disease means that the kidneys have been irreversibly damaged due to unknown causes or due to causes that are not well controlled (e.g. diabetes and high BP). When the kidneys are damaged, waste products accumulate in the blood, there is a disturbance in fluid, electrolytes and acid base balance and blood pressure becomes high. Other complications of CKD include anemia (low blood count), weak bones and poor nutritional health. These problems happen slowly, over a long period of time, often without symptoms. Eventually, CKD progresses to kidney failure requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant to maintain life. Kidney disease also increases risk of heart attack and stroke. Early detection and treatment can prevent or delay these complications.
How does one know if he/she has CKD?
As mentioned earlier, CKD is often asymptomatic. The most common manifestation of CKD is high BP. Therefore, anyone who has high BP must get checked for kidney disease. Other common manifestation is intermittent or continuous swelling of the legs which is often ignored.Three simple tests will confirm CKD. These include:
1. Persistent presence of proteins on urine routine examination (normally there should be no proteins in the urine).
2. Persistently elevated creatinine (a breakdown product of muscle excreted by the kidney) in the blood.
3. Small, echogenic kidneys on ultrasound. This is a definite indicator of CKD. Once ultrasound shows kidneys to be small and echogenic, one must accept diagnosis of CKD.
How is CKD treated?
The first step in treatment of CKD is to identify the cause and treat the cause if treatable. The next step is to treat all the complications associated with CKD. This means controlling BP, fluid, electrolyte, acid base, calcium and phosphorus disturbance, and correcting anemia (low hemoglobin).Not all patients with CKD will have all the complications. Therefore, treatment has to be individualized. A diet low in protein is useful in those with slowly progressive CKD and only if the appetite and nutritional status of the patient is good. There is no fixed diet. It must be individualized for each patient depending on his/her condition.A very important part of management is to avoid doing anything that can further damage the kidneys. Taking pain killers like ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxen, mefenamic acid etc.accelerate rate of loss of kidney function. Taking alternative therapies about which details are not known also can result in faster loss of kidney function. The best principle is to take as few medicines as possible and only those required to treat the complications of CKD.
Also read: Why Ayurveda Should be the First Choice for Chronic Kidney Disease
How are high blood pressure and kidney disease related?
They are related in two ways:
1. High blood pressure is a leading cause of CKD. Over time, high blood pressure can damage blood vessels throughout our body. This can reduce the blood supply to the kidneys. High blood pressure also damages the tiny filtering units in the kidneys. As a result, the kidneys start failing.
2. High blood pressure can also be a complication of CKD. Kidneys play a key role in keeping blood pressure in control. Diseased kidneys are less able to regulate blood pressure. As a result, blood pressure increases. Therefore, as mentioned earlier, everyone with high BP must get kidneys checked. A good control of BP can significantly slow down the rate at which kidney function worsens.
(Disclaimer: Dr Bharat V Shah is Director, Institute of Renal Sciences, Global Hospital, Mumbai. Views expressed are a personal opinion)
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter , Instagram.