An NABH accreditation marks a milestone in any hospitals growth story. Typically a healthcare organisation is uated against 100 standards and 503 objective elements contained in 10 chapters. The following approach paper enumerates ICT functions that are taken into account for in the accreditation process.
Dr Vinoy Singh : Head – Health Informatics Srishti Software


National Accreditation Board for Hospitals (NABH), a constituent board of Quality Council of India (QCI), have come up with standards for accrediting Hospitals with an aim to provide a framework for quality assurance and quality improvement. The intent of the standards is to provide information to patients about the level of healthcare an institution can or cannot provide.

NABH standard definition covers 10 criteria groups � first five are patient centric and the next five are organisation centric.

Relevant ICT technologies/functionalities facilitating compliance to these standards are mentioned below, grouped as per NABH criteria.
-
Access, Assessment and Continuity of Care (AAC) Criteria Group
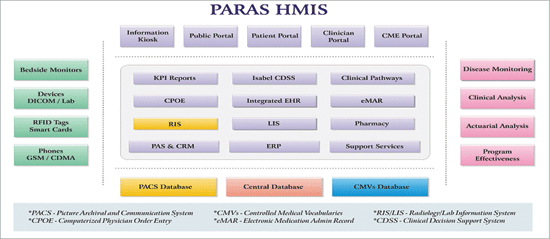
 Standards for ‘Registration’, ‘Admission’, ‘Discharge’, ‘Transfer’ and ‘Referral’ processes are covered in this group and are taken care of by using the Patient Administration System (PAS) module of a Health Management Information System (HMIS). This functionality forms one of the basic blocks of a modern HMIS (refer figure 1).Standard Clinical Assessment, including alerts for Allergy, ADR and Critical Problems are greatly assisted by use of ICT. Life critical information related to Allergy or ADR once captured is available across all the points of care in a hospital, thereby improving standards of care to a great extent and also preventing life threatening mistakes.
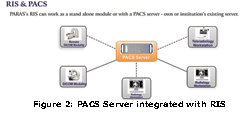
Standards for ‘Registration’, ‘Admission’, ‘Discharge’, ‘Transfer’ and ‘Referral’ processes are covered in this group and are taken care of by using the Patient Administration System (PAS) module of a Health Management Information System (HMIS). This functionality forms one of the basic blocks of a modern HMIS (refer figure 1).Standard Clinical Assessment, including alerts for Allergy, ADR and Critical Problems are greatly assisted by use of ICT. Life critical information related to Allergy or ADR once captured is available across all the points of care in a hospital, thereby improving standards of care to a great extent and also preventing life threatening mistakes.Standardised Lab and Imaging services are covered through Laboratory Information System (LIS) and Radiology Information System (RIS). RIS systems either standalone or as a part of a modern HMIS, consist of a Picture Archival and Communication System (PACS) Server which is connected to different workstations (refer to figure 2).
Figure 2: PACS Server integrated with RIS
-
Patient Rights and Education (PRE)
 Standards related to ‘Consent Recording/Archiving’ are an important constituent of this group. Using ICT can not only help print and use situation specific consent forms (using templates saved in the application) but also scan the signed forms and save it in the application, making them available across time and space.
Standards related to ‘Consent Recording/Archiving’ are an important constituent of this group. Using ICT can not only help print and use situation specific consent forms (using templates saved in the application) but also scan the signed forms and save it in the application, making them available across time and space. -
Care of Patients (COP)
By using speciality specific Clinical ‘Packs’, ICT ensures a standardised delivery of clinical care across all locations and departments of a hospital. Using Clinical Process Guidelines (CPG) modern EHR systems provide a ‘workflow template’, using which healthcare professionals traverse a pre-charted path and thereby ensure a standard model of care. -
Management of Medication (MOM)
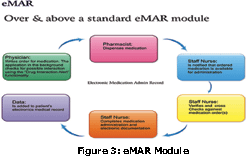
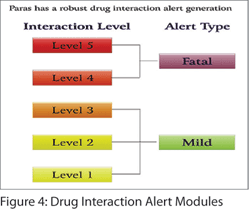 Healthcare professionals need assistance while choosing a medication from a large list of medications available with respect to Drug Interaction and ‘Individual Sensitivity’. This is usually very difficult to achieve if the process is manual and the consultant is relying totally on his memory. Modern HMIS take care of this need through a ‘Pharmacy’ module working closely along with a ‘Medication Interaction Alert’ module and an ‘Electronic Medication Administration Recording (eMAR) module. (Figure 3 & 4)
Healthcare professionals need assistance while choosing a medication from a large list of medications available with respect to Drug Interaction and ‘Individual Sensitivity’. This is usually very difficult to achieve if the process is manual and the consultant is relying totally on his memory. Modern HMIS take care of this need through a ‘Pharmacy’ module working closely along with a ‘Medication Interaction Alert’ module and an ‘Electronic Medication Administration Recording (eMAR) module. (Figure 3 & 4) -
Hospital Infection control (HIC)
Two important HMIS modules which cover the standards covered in this section are ‘Central Sterilisation and Store Department’ (CSSD) module and ‘Bio Medical Waste management’ Module. -
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
An intelligent HMIS, which is capable of reporting ‘Key Performance Indicators’ assists in achieving the standards mentioned in this section. -
Responsibilities of Management (ROM)
It is very difficult to achieve these functionalities without ICT. A modern HMIS is capable of creating a hierarchy of ‘Roles’ with robust ‘Role Based Security Rules’ thereby ensuring proper accountable Hospital Management. -
Facilities Management and Safety (FMS)
A ‘Materials Management System’, which includes Stores Management, takes care of all the processes related to Equipment and Devices life cycle. -
Human Resource Management (HRM)
A standard functionality mapping of an HRM module in an HMIS is necessary to meet these standards. -
Information Management System (IMS)
A modern HMIS takes care of the information needs of the care providers, management of the organisation as well as other agencies that require data and information from the organisation.
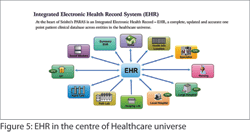 Complete and accurate medical record is maintained for every patient, which also covers ‘Continuity of Care’. Confidentiality, integrity and security of information are maintained. Policies and procedures related to retention time of records, data and information can be enforced. Medical Audit can be performed. EHR functionality is shown above (Figure 5).
Complete and accurate medical record is maintained for every patient, which also covers ‘Continuity of Care’. Confidentiality, integrity and security of information are maintained. Policies and procedures related to retention time of records, data and information can be enforced. Medical Audit can be performed. EHR functionality is shown above (Figure 5).
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter , Instagram.
"Exciting news! Elets technomedia is now on WhatsApp Channels Subscribe today by clicking the link and stay updated with the latest insights!" Click here!






