 Health IT and medical technology are together playing a critical role in changing the face and fate of the healthcare. Monalisa, ENN, explores the current scenario and growth potential of both the segments
Health IT and medical technology are together playing a critical role in changing the face and fate of the healthcare. Monalisa, ENN, explores the current scenario and growth potential of both the segments
The availability of advanced medical technology, backed by apt usage of Information Technology, has expanded both the reach as well as scope of healthcare services. The industry is witnessing a subtle, tectonic shift from symptomatic to predictive healthcare delivery model.
Rising demand for healthcare quality, better access, cost reductions, higher operational efficiencies and lower medical errors are acting as catalysts for the adoption of technology by healthcare providers. Coupled with this is the growing exposure of patients to global health standards and their increasing consciousness for preventive healthcare. Adoption of innovative and cost-effective solutions is thus increasingly becoming imperative for healthcare providers.

Rising IT Expenses

No wonder, IT is gradually gaining prominence in the spending of healthcare providers and enterprises. As per a report by Gartner, healthcare providers in India will spend `57 billion on IT products and services by the end of 2013, an increase of seven percent from `53 billion in 2012. This includes spending on internal IT (including personnel), hardware, software, external IT services and telecommunications.
The report titled, Enterprise IT Spending for the Healthcare Providers Market, Worldwide, 2010-2016, further mentions that Telecommunications will remain the largest overall spending category, that is likely to reach `17.2 billion in 2013 from `16.6 billion in 2012 at a growth rate of 3.9 percent.
Hospital Information Systems (HIS), Picture Archiving and Communications Systems (PACS), Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) and Mobile Technologies will be high on the agenda, says Anurag Gupta, Research Director at Gartner. We expect to see providers benefit by offering cost-effective business models which show quick returns on capital by improving patient coverage and improving quality of care. Health insurance growth will also catalyse technology adoption in healthcare provider segments, he adds.

Health IT Trends
Initiatives are currently focused on Digital Health Records, Telemedicine and Mobile Delivery of healthcare information. Also, the industry is moving towards a patient-centric approach that enables comparison of prices and quality of medical providers through social networking and other such platforms. Besides, the industry is gradually harnessing the potential of disruptive technologies such as cloud computing and big data. KPMG, in a study titled Six Converging Technology Trends 2013 identifies six disruptive technological innovations, namely “ big data, cloud computing, social media, mobility, embedded systems and augmented reality “ that are likely to revamp the face of the healthcare sector. Big data: New technologies in healthcare management systems consist of electronic data storage, data maintenance and exchange. However, data poses its own set of challenges in terms of volume (large quantities of data), variety (structure and unstructured), and velocity (rate of data generation). Big data analytics platforms shall prove effective in extracting intelligence from humungous patient records. Cloud: High initial costs, need for human resources to maintain the systems and need for accessibility of data 24/7 often act as deterrents for healthcare providers in the adoption of technology. Cloud computing offers answer for all such issues. EMRs, telemedicine, patient management, and medical imaging are gradually shift- ing to cloud. Cloud services can now also be integrated with special medical hardware (embedded systems) for remote patient monitoring.
However, a growing concern in the adoption of cloud lies in the uncertainty whether hospitals and clinics will trust their data to be stored offsite. Ernst & Young reports that in India, some players are looking to build their own networks. It predicts that initially, private cloud is more likely to be adopted, as opposed to the public cloud, where hospitals have to share data externally.

Telecommunications will remain the largest overall spending category under Health IT, reaching up to `17.2 billion in 2013, at a growth rate of 3.9 percent
Social media: Social media tools are gaining popularity, serving as an easy and cost-effective solution for both patients and healthcare providers, who can now monitor patients in a virtual environment. It also transforms the patient-doctor communication from one-to-one to one-tomany, whereby doctors reach out to a number of online users at a go using the Internet.
mHealth: Right from viewing results, to ordering medicines, e-prescribing, or remote monitoring “ mHealth can play a vital role in efficient patient management and quicker handling of emergency situations. Blurring lines and convergence of wireless communications, embedded systems, social networks and enabling technology of cloud computing will further propel the adoption of mobile health technologies. Mobile technology represents a high-reach, cost-efficient method for making health care more accessible, affordable and effective across the developing world.
Embedded systems: Embedded systems and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) technology have made automated medical devices that focus on disease prevention and healthy living a reality. A number of embedded software companies and telecom operators are developing technologies to improve patient care. KPMG reports that the market is booming with a number of start-ups in Silicon Valley, application developers, carriers such as Vodafone, Deutsche Telekom, AT&T, Verizon, China Mobile, and France Telecom and giants such as IBM, General Electric and Philips. Augmented reality: In the field of academics, augmented reality can be used by medical students to practice surgery in a controlled environment. With 3D imagery and interactive display, complex medical conditions can be explained to patients using visualisation aids.
Consolidated Platforms
The Health IT industry is expected to witness a convergence of technologies in the future, leading to an increased demand for consolidated platforms KPMG in India Analysis predicts that the convergence is likely to be more in the areas of disruptive technologies such as cloud, mobility, social media and big data as there is a clear upcoming trend of Tele-health and Webhealth. Although some players are already heading in this direction through platforms such as SOMOCLO (Social Media, Mobility and Cloud), the trend is yet to gain momentum on a large scale. Augmented reality would also have applications, however, lesser in comparison to other disruptive technologies. AR applications would be more focused in medical education rather than actual patient treatment and care.
Big data analytics shall prove effective in extracting intelligence from humungous patient records
Medical Technology
While health IT is reducing operational costs and enhancing efficiency of healthcare providers, medical tech-nology is playing a strategic role in fostering better healthcare delivery. According to the European Medical Technology Industry Association, billions of patients worldwide depend on medical technology at home, at the doctors clinic and in hospitals. The medical technology market in India was valued at USD 2.75 billion in 2008 (NIPER Ahmedabad) and is likely to reach USD 14 billion in 2020 at a CAGR of approximately 15 percent (Industry Analysis, PwC estimates). Broadly segmented into medical equipments, implants, and medical disposables & furniture, the medical technology market offers a wide range of products ” from contact lenses and insulin pens to pacemakers, MRI scanners, prostheses, life-support machines and so on. With recurrent technology breakthroughs, the pace of medical invention is accelerating, resulting in better clinical outcomes, lesser invasive procedures and shorter recovery times, hence improving overall health of people. According to a PwC report titled, Enhancing access to healthcare through innovation ” Medical technology in India, the future of medical technology innovation is bright and India and China will be the stars of the 21st century. The report further states that the epicenter of innovation ecosystem is shifting towards emerging economies such as India. In the future emerging economies will have a higher spending on R&D in future providing the trigger for innovation.
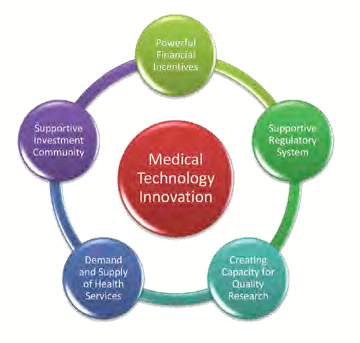
FIVE PILLARS FOR INNOVATION
Key Challenges
Although the future seems promising, the Indian medical technology industry is currently plagued by multiple challenges. On one hand, the industry is fiercely fragmented with the presence of both domestic firms as well as MNCs. Also, the market is highly imports-
driven which constitute and of about 75 percent of the market. Highend medical technology products, such as imaging equipments, pacemakers, orthopaedic and prosthetic appliances, breathing and respiration apparatus, and dental equipments are largely imported by MNCs into India, giving a tough competition to indigenous players. Moreover, the per capita spending of USD 2 on medical technology in India is significantly lower than other developing economies. Demand in India is predominantly driven from the Tier-I cities. The challenge lies in entering into smaller towns and rural areas, where penetration has remained low due to lack of affordability (for such products), accessibility (of healthcare services), awareness (about medical technology) and availability.
Way Forward
Given the criticality of the situation, innovations in products alone wont be enough. There is a serious need to rethink and redesign the entire business model. Medical technology industry needs to evolve from merely supplying devices and equipments, to providing integrated solutions for improving health outcomes.
PwC analysis has identified five pillars on which medical technology innovation shall rest, depending of on how strong these pillars are and how well they interact with each other. These include: Powerful financial incentives; Creating capacity for quality research; Supportive regulatory system; Demand and supply of health services; and Supportive investment community.
A collaborative approach towards innovation is needed, whereby all stakeholders, including the patients, medical centres, the industry, academia, healthcare providers, health insurance companies and the government should come together to promote medical
technology innovation in India.
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter , Instagram.
"Exciting news! Elets technomedia is now on WhatsApp Channels Subscribe today by clicking the link and stay updated with the latest insights!" Click here!
















